India’s road infrastructure has improved greatly in the last decade due to the government’s efforts. Key initiatives focus on better highways, rural connectivity, road safety, and sustainability, aiming to create a strong, connected transport system.
Capital Expenditure Surge
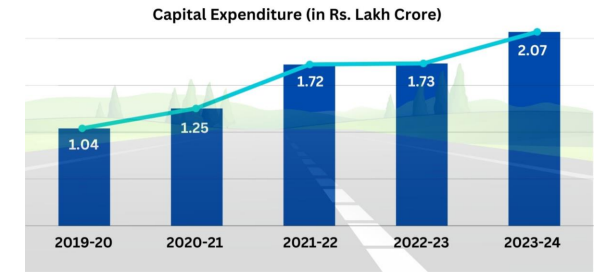
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has significantly increased its capital expenditure over the past five years, reflecting the government’s commitment in enhancing the national highways network and infrastructure. Details of Capital Expenditure incurred by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) in
last five years is as under:
Road Network Expansion
A key component of this effort is the Bharatmala Pariyojana, under which projects are executed in categories such as Economic Corridors Development, Inter-corridor and Feeder Routes Development, National Corridors Efficiency Improvement, Border and International
Connectivity Roads, Coastal and Port Connectivity Roads, and Expressways.
This flagship program has awarded 26,425 km and constructed 17,411 km of roads until March 2024, with an expenditure of Rs. 4.59 lakh crore as of March 31, 2024
Enhancing Highway Infrastructure
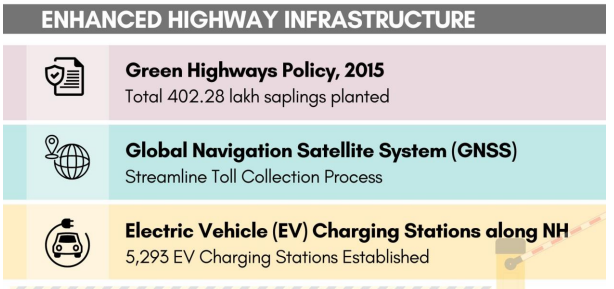
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) issued the Green Highways (Plantation, Transplantation, Beautification & Maintenance), Policy- 2015 to promote environmental sustainability.
As of July 24, 2024, the pilot study for a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) based user fee collection system has been completed on two key highway stretches. This new system aims to streamline toll collection processes and improve efficiency.
Additionally, in a significant step towards supporting electric mobility, a total of 5,293 Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations have been established along National Highways.
Road and Bridge Maintenance and Safety
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways allocates Central Road Infrastructure Fund (CRIF) to State Governments and Union Territories for the development and maintenance of State Roads.
To ensure the structural integrity of National Highways and their bridges, the further mandates both visual and equipment-based periodical inspections, evaluations, and monitoring.
Dedicated Emergency Response Teams, equipped with adequate manpower and machinery, are deployed at landslide-prone sites. Advanced Traffic Management Systems (ATMS) and the Rajmaarg Yatra App are also utilized to disseminate critical information and assist
National Highway users.
Conclusion
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways’ efforts and government initiatives show a strong commitment to improving India’s road infrastructure, which will boost the economy and enhance citizens’ quality of life.



